Medical
Medical Sector Metal Solutions: Strength, Precision, and Reliability
Supra Alloys provides high-quality aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and nickel products in plate, sheet, and bar forms tailored for the medical sector. These materials meet the rigorous standards required for precision, biocompatibility, and durability in healthcare and medical device applications.
 Aluminum Plate, Sheet, Bar, and Custom Extrusions – Precision for Medical Applications
Aluminum Plate, Sheet, Bar, and Custom Extrusions – Precision for Medical Applications
Aluminum Sheets and Plates
High-strength alloys like 2024, 7075, and 6061 are widely used in medical imaging equipment, surgical tables, and structural components for diagnostic devices. These materials provide excellent strength-to-weight ratios, ensuring durability without adding unnecessary weight.
Extruded Aluminum Profiles
Custom extrusions from 6061 and 6063 are ideal for lightweight frames in medical equipment such as mobile diagnostic carts, IV stands, and modular operating room structures.
Aluminum Tubing and Castings
Tubing systems made from 6061 or 6063 alloys are critical in medical mobility devices like wheelchairs and stretchers. Cast aluminum components, such as those from A356, are used for housing medical equipment and support brackets.
Fasteners and Components
Aluminum fasteners from 2024 or 7075 alloys are used in medical devices requiring lightweight, corrosion-resistant connections, such as in robotic surgical systems and implantable equipment.
Nickel Plate, Sheet, Bar – Durability and Performance for High-Tech Medical Devices
Surgical Tools and Implants
Nickel superalloys such as Inconel 625 and 718 are used in surgical instruments and high-performance implants due to their strength, corrosion resistance, and durability under repetitive use.
Power Systems and Batteries
Nickel-based materials are integral to power storage in medical devices such as implantable defibrillators and pacemakers, ensuring reliable and long-lasting energy.
Cryogenic Systems
Nickel alloys like Invar are used in cryogenic storage systems for biological materials, ensuring stability under extreme temperature variations.
Medical Imaging and Electronics
Nickel’s conductivity and resistance to wear make it ideal for components in advanced imaging systems, circuit boards, and sensors used in diagnostic devices.
Stainless Steel Plate, Sheet, Bar, and Custom Extrusions – Precision and Hygiene
Stainless Steel Plates
Plates from grades like 321 and 316 are used for high-stress components such as surgical tables, autoclaves, and patient transfer systems. These plates provide strength and resistance to sterilization processes.
Stainless Steel Sheets
Sheets are used for medical-grade sinks, countertops, and interior panels for operating rooms, ensuring easy cleaning and maintaining a sterile environment.
Stainless Steel Bars
Bars are machined into surgical tools, robotic arms, and fasteners for medical devices. Their high strength and corrosion resistance ensure reliable performance over repeated use and sterilization cycles.
Custom Extrusions
Stainless steel extrusions are employed in modular frameworks for diagnostic carts, medical bed frames, and structural supports, ensuring durability and adaptability.
Advancing Medical Excellence
Supra Alloys’ diverse range of metals supports the medical sector’s innovation and growth. Whether for lightweight aluminum components, biocompatible titanium implants, durable nickel systems, or hygienic stainless steel solutions, our materials empower cutting-edge medical technology and patient care.
Titanium Plate, Sheet, Bar – Biocompatibility and Strength for Medical Innovation
Implants and Prosthetics
Titanium alloys, particularly Ti-6Al-4V, are prized for their biocompatibility and strength, making them the material of choice for orthopedic implants, dental implants, and prosthetic components.
Surgical Instruments and Equipment
Titanium plates and sheets are used for manufacturing lightweight yet durable surgical instruments and diagnostic equipment. Their corrosion resistance ensures longevity in sterilization environments.
Medical Device Housings and Radiation Shielding
Titanium panels provide structural support and radiation shielding for imaging equipment like CT and MRI machines, protecting sensitive components and ensuring patient safety.
Fasteners and Connectors
Titanium fasteners and connectors are used in implant assemblies and medical robotics, delivering strength and precision in critical applications.
Medical Grade Titanium
Titanium 6AL4V and 6AL4V ELI, alloys made of 6% Aluminum and 4% Vanadium, are the most common types of titanium used in medicine. Because of its harmonizing factor with the human body, these titanium alloys are popularly used in medical procedures, as well as in body piercings. Also known as Gr. 5 and Gr. 23, these are some of the most familiar and readily available types of titanium in the US, with a number of distributors specializing in these specific grades.
Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-6Al-4V ELI offer greater fracture-resistance when used in dental implants. The implant procedure begins with the insertion of a titanium screw into the jaw. The screw resembles and acts like the root of the tooth. After an allotted amount of time has passed for the bone to have grown into the medical grade titanium screw, a fake tooth is connected to the implant.
Benefits of Medical Titanium
- Strong
- Lightweight
- Corrosion Resistant
- Cost-efficient
- Non-toxic
- Biocompatible (non-toxic AND not rejected by the body)
- Long-lasting
- Non-ferromagnetic
- Osseointegrated (the joining of bone with artificial implant)
- Long range availability
- Flexibility and elasticity rivals that of human bone

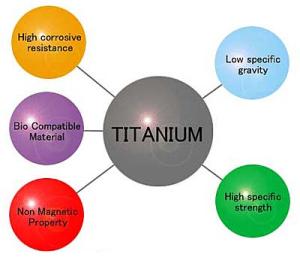
Two of the greatest benefits of titanium are its high strength-to-weight ratio and its corrosion resistance. Couple this with its non-toxic state and its ability to fight all corrosion from bodily fluids and it’s no wonder titanium has become the metal of choice within the field of medicine.
Titanium is also incredibly durable and long-lasting. When titanium cages, rods, plates and pins are inserted into the body, they can last for upwards of 20 years. And dental titanium, such as titanium posts and implants, can last even longer.
Another benefit to titanium for use in medicine is its non-ferromagnetic property, which allows patients with titanium implants to be safely examined with MRIs and NMRIs.
Osseointegration is a unique phenomenon where your body’s natural bone and tissue actually bond to the artificial implant. This firmly anchors the titanium dental or medical implant into place. Titanium is one of the only metals that allows for this integration.
Uses of Medical Titanium
Most all of us know someone who has required orthopedic surgery to replace a failing hip socket, shoulder joint or severely broken bone. It’s very likely medical grade titanium was the material of choice for the surgeons when reconstructing these parts of the body. As evidenced in the previous section, natural titanium properties make it a perfect alloy to be used within the body.
Medical grade titanium is used in producing:
- Pins
- Bone plates
- Screws
- Bars
- Rods
- Wires
- Posts
- Expandable rib cages
- Spinal fusion cages
- Finger and toe replacements
- Maxio-facial prosthetics
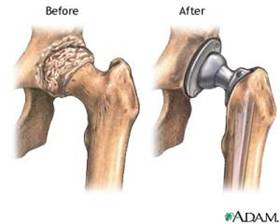
Some of the most common uses for titanium are in hip and knee replacement surgeries. It is also used to replace shoulder and elbow joints and to protect the vertebrae following complicated and invasive back surgery. Titanium pegs are used to attach false eyes and ears and titanium heart valves are even competing with regular tissue valves.
Surgical Titanium Instruments
There are a number of characteristics that make titanium the perfect choice for surgical instrumentation:
-
- It’s harder than some steel, yet lighter in weight.
- It is bacteria resistant.
- Again, it can be used in conjunction with instruments emitting radiation.
- Titanium is incredibly durable, giving instruments greater longevity.
Because of these great properties, it is used to create a number of titanium surgical devices:
-
- Surgical forceps
- Retractors
- Surgical tweezers
- Suture instruments
- Scissors
- Needle and micro needle holders
- Dental scalers
- Dental elevators
- Dental drills
- Lasik eye surgery equipment
- Laser electrodes
- Vena cava clips
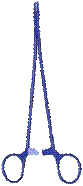
Dental Titanium
As mentioned earlier, titanium has the ability to fuse together with living bone. This property makes it a huge benefit in the world of dentistry. Titanium dental implants have become the most widely accepted and successfully used type of implant due to its propensity to osseointegrate. When bone forming cells attach themselves to the titanium implant, a structural and functional bridge forms between the body’s bone and the newly implanted, foreign object.
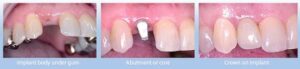
Photo Credit: Dentist in Goa via Flickr
Titanium orthodontic braces are also growing in popularity. They are stronger, more secure and lighter than their steel counterparts. And of course, medical grade titanium’s biocompatibility makes its use in braces even more beneficial than its competing alloys.
Future of Bio-medical Titanium
It is expected that use within the biomedical industry will only continue to grow for titanium in the coming years. With the baby-boomer demographic continuing to age and our health industry pushing for people to live more active lives, it’s only logical that the medical industry will continue researching new and innovative uses for this popular metal alloy. And with health care reform a current major issue, titanium’s cost-efficiency adds even more appeal to those looking to cut health care costs.
About the Author
Craig Schank is General Manager of Supra Alloys, a full-service titanium supplier and processing center headquartered in Camarillo, California. Craig has long experience in the special metals industry, with a particular interest in medical titanium applications.
For more information, contact us via the website at www.Supraalloys.com, call 805.388.2138, or email the author at [email protected].